No | Category | Cutting | Rolling | Annotation |
1 | Pipe thread type & 1:16 taper | "Open-space" thread processing, teeth, especially taper forming is instability | The conical rollers is excellent, durable and wear-resistant tools makes "closed-space" forming, to ensure the thread shape and taper and other dimensions being consistency over and over | When the lathe tool is cutting V-thread, the friction and wear between the blade, the front and the back of the tool and the steel pipe are uneven. The axial movement of the tool when the unstable lathe machine is working will exacerbate this instability |
2 | Dimensional stability of thread in mass production | Tool wear and machine instability can be compensated by numerical control system through empirical data, the effect is not ideal, the production cost is high, and it is difficult to achieve in large-scale production or on-site construction | The long life of the rolling system ensures that the product quality consistency | |
3 | Concentricity | Poor, easy to destroy internal and | Good, self-centering technology, to ensure that the two ends of the pipe thread concentricity is good, easy to install | The concentricity of the inner threaded parts will be required higher and higher |
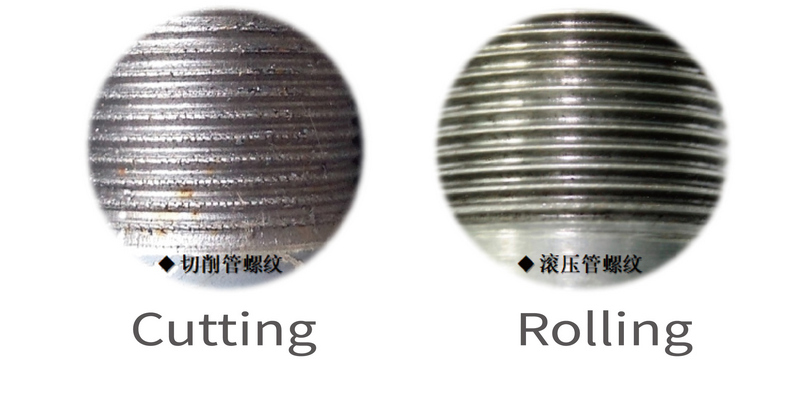
4 | Surface roughness | The point contact between the knife and the steel pipe causes the surface of the thread to be rough, and the spot welding phenomenon that damages both male and female threads during large torque-tightening | The roller is in contact with the steel pipe, and the height between the convex and concave peaks and valleys of the thread after forming is 1~4um, which is almost equivalent to grinding | Look-like-grinding roughness makes it fit well with the internal thread. The poor tightness is one of the reasons causing easy leakage of the connection |
5 | Strength of extension | 50% lower than the original steel pipe | Compared with cutting pipe threads, the tensile strength is increased by 150-180% | Compared with the metal fiber in the thread section, the metal fiber in the thread section is extruded and extended by rolling, and the metal grain density is increased. After extrusion, the thread is thick and dense and hardened by cold forming thread, resulting in greatly improved mechanical connection strength of the thread |
Bending strength | 50% lower than the original steel pipe | Compared with cutting pipe threads, the bending strength is increased by 150-170% | ||
Shear strength | 50% lower than the original steel pipe | Compared with cutting pipe threads, its shear resistance is increased by 140~170% | ||
Fatigue resistance | 200% lower than the original steel pipe | Compared with cutting pipe thread, its fatigue strength is increased by 250~400% | ||
6 | Thread surface strength | The friction heating of steel pipe causes the hardness of thread surface to decrease | Compared with the cutting thread, the surface hardness is increased by 130% | |
7 | Pressure bearing capacity of | 50% lower than the original steel pipe | The weight per unit length of the rolled steel pipe thread is equal to that of the original pipe | |
8 | Corrosion resistance of pipe thread section | The hot dip galvanizing layer is 100% removed, and the thread section has no corrosion resistance | The galvanized layer is 100% retained, and the corrosion resistance is equal to that of the original pipe even better | Improved oxidation resistance of thread surface 40 times or more, increasing corrosion resistance of joints |
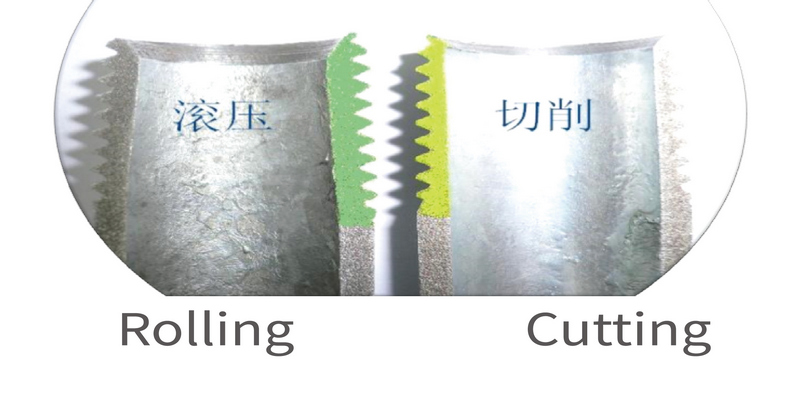
The metal fibers are cut, and the surface is "scarred" with high roughness | The grain structure density of the steel pipe in the thread section is increased from grade 6 to 8.5 |